Cloud storage refers to a type of online storage service that allows users to store and manage their digital data, such as files, documents, photos, videos, and other types of data, in a remote server or data center hosted by a cloud service provider. Cloud storage enables users to store their data securely in the cloud, and access it from anywhere with an internet connection, using various devices, such as computers, smartphones, or tablets.
Cloud storage services typically provide a scalable and flexible storage solution, where users can store and retrieve data as needed, and pay for the storage capacity and usage based on a subscription or pay-as-you-go model. Cloud storage services are commonly used for personal or business purposes, as they offer several advantages over traditional local storage solutions, such as physical hard drives or on-premises servers, including:
- Scalability: Cloud storage allows users to scale their storage capacity up or down as needed, without having to invest in physical hardware or manage storage infrastructure. This makes it easy to accommodate changing storage requirements and ensures that users only pay for the storage they actually use.
- Accessibility: Cloud storage enables users to access their data from anywhere with an internet connection, using various devices, making it convenient for remote or mobile access. It also facilitates easy sharing and collaboration with others, as files can be shared or synced with multiple users or devices.
- Reliability and durability: Cloud storage services typically offer high levels of data redundancy, replication, and backup, which helps ensure data durability and availability. Cloud service providers also invest in robust infrastructure and data protection measures to safeguard data against hardware failures, disasters, or data loss.
- Cost-effectiveness: Cloud storage services are typically cost-effective, as users can pay for storage capacity based on their actual usage, without the need for upfront investment in hardware or infrastructure. This makes it suitable for businesses of all sizes, as it enables cost optimization and budget flexibility.
- Security: Cloud storage services often offer robust security measures, such as data encryption, access controls, and authentication, to protect data from unauthorized access or data breaches. Cloud service providers also comply with industry standards and regulations related to data security and privacy.
- Backup and disaster recovery: Cloud storage can be used as a backup and disaster recovery solution, as data stored in the cloud can be replicated and backed up in multiple locations, reducing the risk of data loss due to hardware failures, disasters, or other unforeseen events.
- Integration with other cloud services: Cloud storage services are often integrated with other cloud-based services, such as file sharing, content management, or application hosting, allowing for seamless integration and workflow automation.
Overall, cloud storage provides a flexible, scalable, cost-effective, and convenient solution for storing and managing digital data, making it popular for personal and business use cases. However, it’s important to consider the security and privacy aspects of cloud storage, and choose a reputable cloud service provider that meets your specific requirements and compliance needs.
How Clouds Storage Works
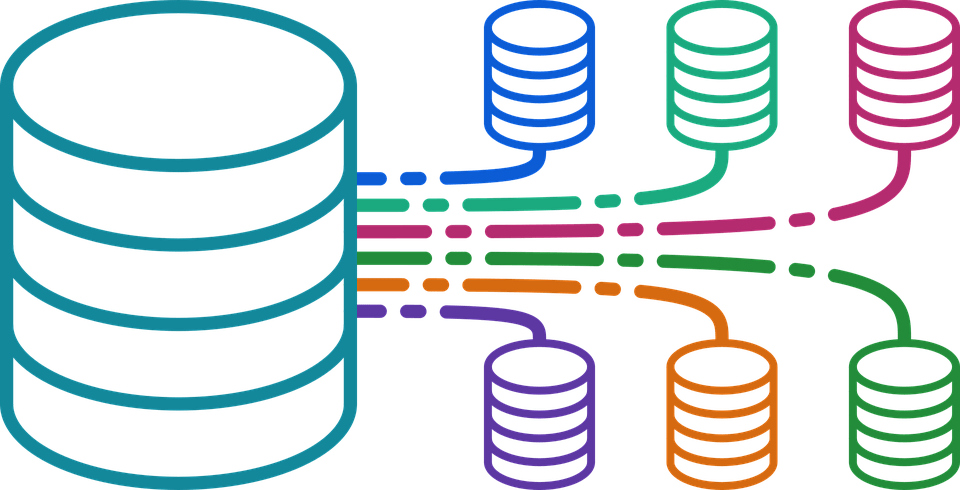
Cloud storage works by storing data in remote servers or data centers that are owned and operated by a cloud service provider. These servers are typically located in geographically distributed data centers to ensure data redundancy and availability. When a user uploads data to the cloud storage service, the data is stored in these remote servers and can be accessed and managed from anywhere with an internet connection using various devices, such as computers, smartphones, or tablets. Here’s a general overview of how cloud storage works:
- Data Upload: Users can upload their data, such as files, documents, photos, videos, and other types of data, to the cloud storage service using web-based interfaces, APIs (Application Programming Interfaces), or dedicated client applications provided by the cloud service provider. The data is transmitted over the internet and stored in the cloud storage provider’s servers.
- Data Storage: Once the data is uploaded, it is stored in the cloud storage provider’s servers, which are typically located in multiple data centers across different geographic locations. The data may be replicated or backed up to ensure data durability and availability in case of hardware failures, disasters, or other unforeseen events. The cloud storage provider manages the infrastructure, hardware, and maintenance of the servers.
- Data Retrieval: Users can retrieve their data from the cloud storage service using various methods, such as web-based interfaces, APIs, or client applications. The data is transmitted over the internet and can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, using different devices.
- Data Management: Cloud storage services typically provide various data management features, such as file organization, versioning, sharing, syncing, and access controls. Users can organize their data into folders, apply permissions and access controls to control who can access or modify the data, and manage versions of files to track changes or roll back to previous versions.
- Data Security: Cloud storage services typically provide security measures to protect data from unauthorized access, data breaches, or data loss. These measures may include data encryption, access controls, authentication, monitoring, and auditing. However, it’s important for users to also implement proper security practices, such as using strong passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, and managing access controls, to ensure the security of their data in the cloud.
- Billing and Usage: Cloud storage services typically offer various pricing models, such as pay-as-you-go, subscription-based, or tiered pricing, based on factors such as storage capacity, data transfer, and features. Users are billed based on their usage, and can monitor their usage through usage metrics or billing dashboards provided by the cloud service provider.
Cloud storage offers a flexible, scalable, and convenient solution for storing and managing data in the cloud, and has become widely popular for personal and business use cases. However, it’s important for users to understand the specific features, limitations, and security measures provided by the cloud storage service they are using, and follow best practices for data security and management to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their data in the cloud.
Whats the Price For Clouds Storage
The price for cloud storage varies depending on the cloud service provider, the amount of storage capacity needed, the region or location where the data is stored, the data transfer or bandwidth usage, and any additional features or services included in the storage plan. Here are some common pricing factors for cloud storage:
- Storage Capacity: Cloud storage providers typically offer different tiers or plans with varying storage capacities, ranging from a few gigabytes (GB) to terabytes (TB) or petabytes (PB) of data storage. The cost of cloud storage increases with the amount of storage capacity needed.
- Data Transfer/Bandwidth Usage: Cloud storage providers may charge for data transfer or bandwidth usage, which refers to the amount of data that is transferred in and out of the cloud storage service. This includes uploading data to the cloud storage service and downloading or accessing data from the service. Data transfer or bandwidth charges may vary based on the amount of data transferred or the region where the data is transferred.
- Service Level Agreement (SLA): Some cloud storage providers offer different service levels or performance guarantees, such as availability, durability, or latency, which may impact the cost of the storage plan. Higher service levels or performance guarantees may come with higher costs.
- Additional Features/Services: Cloud storage providers may offer additional features or services, such as data encryption, data management tools, access controls, and integration with other cloud services, which may have additional costs associated with them.
- Subscription Model: Cloud storage providers may offer different pricing models, such as pay-as-you-go, subscription-based, or prepaid plans. Pay-as-you-go plans typically charge based on actual usage, while subscription-based or prepaid plans may provide discounts or other benefits for longer-term commitments.
- Cloud Service Provider: Different cloud service providers may have different pricing structures based on their offerings, infrastructure, and market competition. It’s important to compare pricing from different cloud service providers to find the best fit for your storage needs and budget.
It’s worth noting that cloud storage pricing can be complex and may involve various factors and usage patterns, so it’s important to review the pricing details provided by the specific cloud service provider you are considering, and carefully evaluate your storage requirements to estimate the potential costs accurately. It’s also essential to monitor and manage your usage to avoid unexpected costs, and be aware of any potential additional charges or fees associated with the cloud storage service you choose.
Who are the top clouds storage providers
As of our knowledge cutoff date in September 2021, some of the top cloud storage providers are:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) S3: AWS S3 is a popular and widely-used cloud storage service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS), offering scalable, durable, and secure object storage. AWS S3 is known for its high reliability, performance, and integration with other AWS services.
- Google Cloud Storage: Google Cloud Storage is a cloud storage service provided by Google Cloud Platform (GCP), offering flexible and scalable storage for objects, files, and backups. Google Cloud Storage is known for its global availability, low latency, and integration with other GCP services.
- Microsoft Azure Blob Storage: Azure Blob Storage is a cloud storage service provided by Microsoft Azure, offering scalable and secure object storage for unstructured and structured data. Azure Blob Storage is known for its durability, availability, and integration with other Azure services.
- Dropbox: Dropbox is a cloud storage and file synchronization service that is widely used for personal and business purposes. Dropbox offers features such as file sharing, collaboration, and synchronization across devices, and is known for its ease of use and user-friendly interface.
- Box: Box is a cloud storage and content management platform that is popular for business and enterprise use. Box offers features such as file sharing, collaboration, workflow automation, and integration with other business tools, and is known for its focus on security and compliance.
- iCloud: iCloud is a cloud storage service provided by Apple for Apple device users, offering storage for files, photos, videos, and backups across Apple devices. iCloud is known for its seamless integration with Apple devices, and offers features such as automatic backups, synchronization, and sharing across Apple devices.
It’s important to note that the landscape of cloud storage providers is constantly evolving, and there may be other emerging or specialized cloud storage providers that cater to specific use cases or industries. It’s recommended to carefully evaluate the features, pricing, performance, and security aspects of each cloud storage provider to determine the best fit for your specific storage requirements.
What is Cloud Storage
Cloud storage refers to a type of online storage service that allows users to store and manage their digital data, such as files, documents, photos, videos, and other types of data.
How Clouds Storage Works
Cloud storage works by storing data in remote servers or data centers that are owned and operated by a cloud service provider.
Whats the Price For Clouds Storage
The price for cloud storage varies depending on the cloud service provider, the amount of storage capacity needed, the region.